What is Wi-Fi 6 / 6E?
This page explains the basics of Wi-Fi and the features of Wi-Fi 6 / 6E.
Contents
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi Generations
Features of Wi-Fi 6
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi* is a technology developed by John O’Sullivan, an Australian electrical engineer, and his research team in 1997, and is one of the wireless LAN (Local Area Network) standards that enables digital devices such as PCs, smartphones, and gaming devices to be connected to a network as a computer network that interconnects devices within a relatively narrow range.
* Wi-Fi … Abbreviation for Wireless Fidelity.
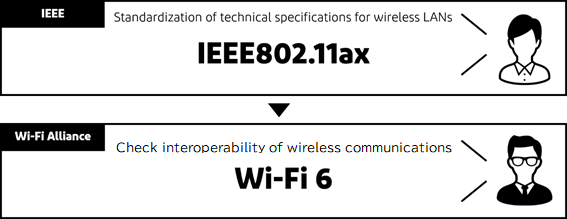
Wi-Fi standardization is mainly composed of two organizations, IEEE and Wi-Fi Alliance.
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE),headquartered in the US, is an organization that standardizes telecommunications-related specifications and has developed various standards, including IEEE802.11, which standardizes technical specifications for wireless LAN. It is the world's largest academic research organization for electrical and electronic technology.
In response to the IEEE802.11-compliant technical specifications for wireless LANs, the Wi-Fi Alliance tests the compatibility of wireless communication between devices using wireless LAN, and grants Wi-Fi certification to those that pass certification tests, thereby enabling interoperability of wireless LAN even amongst different brands of digital devices. The Wi-Fi Alliance tests the interoperability of wireless communications between devices in the use of wireless LAN, and grants Wi-Fi certification to those that pass certification tests.
The Wi-Fi CERTIFIED logo is only approved for use on devices that have passed the Wi-Fi Alliance's interoperability and other certification tests.

Wi-Fi Generations
The names of IEEE802.11-compliant wireless LAN standards are "IEEE 802.11" followed by an alphabetic character to indicate the generation. However, it has been difficult for general users who are not familiar with the IEEE standards to understand which are the new and old communication standards from the name.
In order to make the generations of the standard clearer to understand, the Wi-Fi Alliance has changed the Wi-Fi name for the sixth generation of the Wi-Fi standard, IEEE 802.11ax, to Wi-Fi 6, and the earlier generations, IEEE 802.11n and IEEE 802.11ac, to "Wi-Fi 4" and "Wi-Fi 5" respectively.
There are no generation names for Wi-Fi standards prior to the third generation. Wi-Fi 6E was also introduced by the Wi-Fi Alliance as an extension to Wi-Fi 6, allowing functionality in the unlicensed 6 GHz band in addition to the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bandwidths supported by Wi-Fi 6.
| IEEE Standards | Wi-Fi Generations | Max. Communication Speed | Band Range |
| IEEE802.11 | - | 2 Mbps | 2.4 GHz band |
| IEEE802.11b | - | 11 Mbps | 2.4 GHz band |
| IEEE802.11a | - | 54 Mbps | 5 GHz band |
| IEEE802.11g | - | 54 Mbps | 2.4 GHz band |
| IEEE802.11n | Wi-Fi 4 | 600 Mbps | 2.4 GHz / 5 GHz band |
| IEEE802.11ac | Wi-Fi 5 | 6.9 Gbps | 5 GHz band |
| IEEE802.11ax | Wi-Fi 6 | 9.6 Gbps | 2.4GHz / 5GHz band |
| Wi-Fi 6E | 6 GHz band |
Features of Wi-Fi 6
There are several features of Wi-Fi 6.
- Ultra-high-speed communication
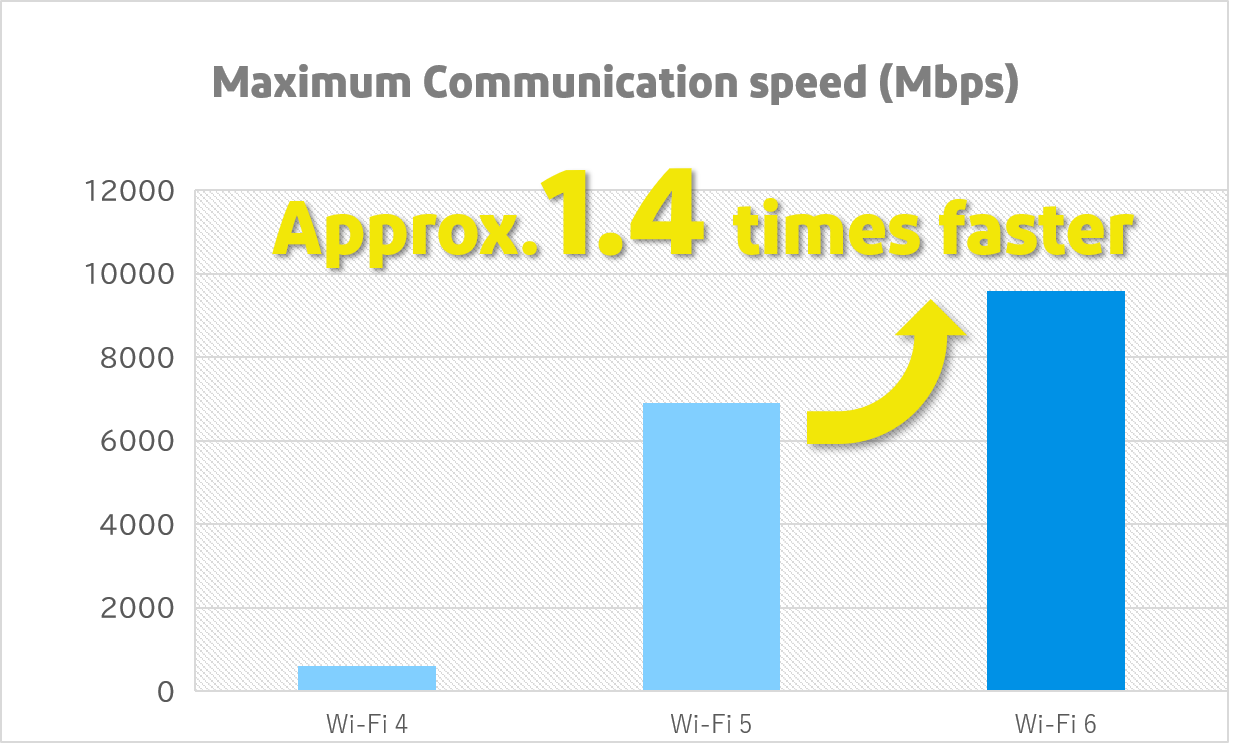
The theoretical maximum transmission speed of Wi-Fi 5 was about 6.9 Gbps though, Wi-Fi 6 is about 1.4 times faster, approx. 9.6 Gbps. As a result, we can view 8K, 4K and other high-quality images and play online games with ease.
- Widened bandwidth
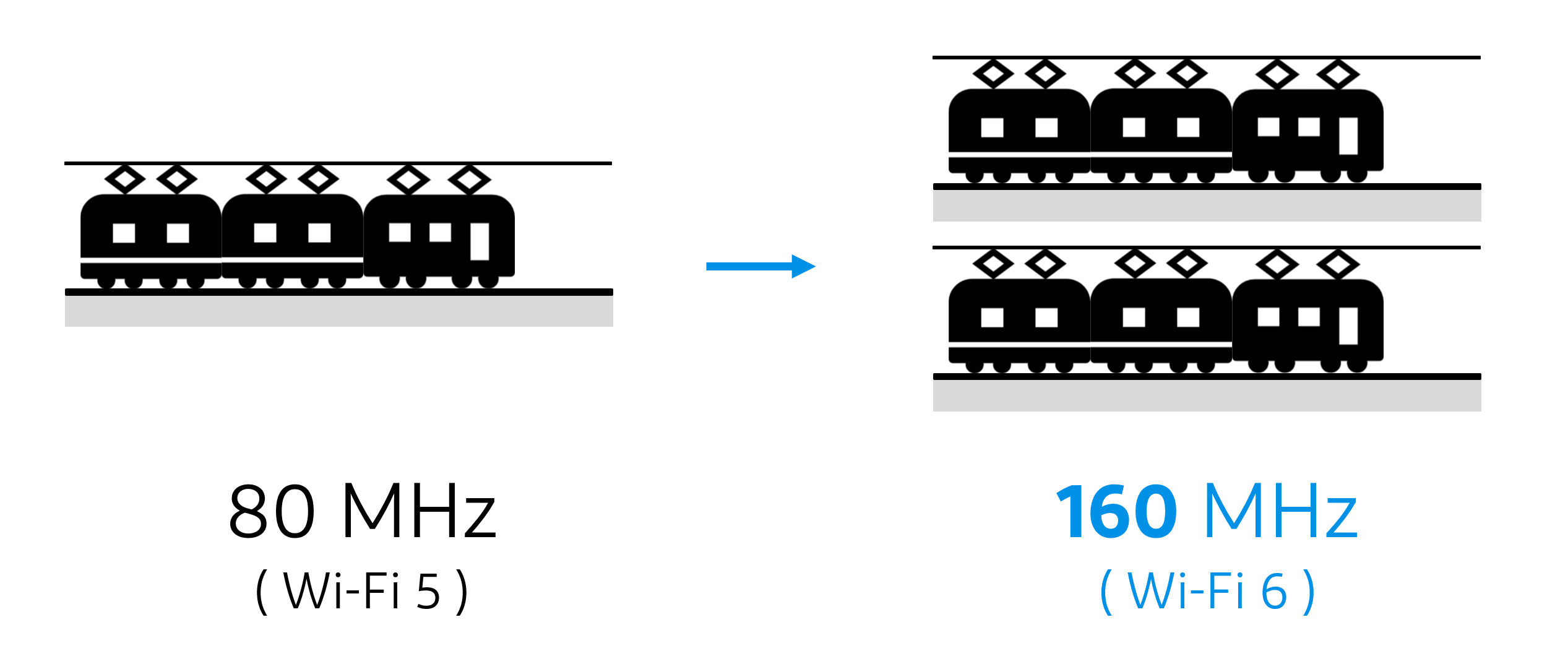
With Wi-Fi 6, bandwidth has been widened from 80 MHz to 160 MHz, increasing the amount of data that can be transmitted at once. As shown in the following image, the amount of data that can be transported increases as the number of routes expands from one to two.
- Simultaneous communication between multiple terminals
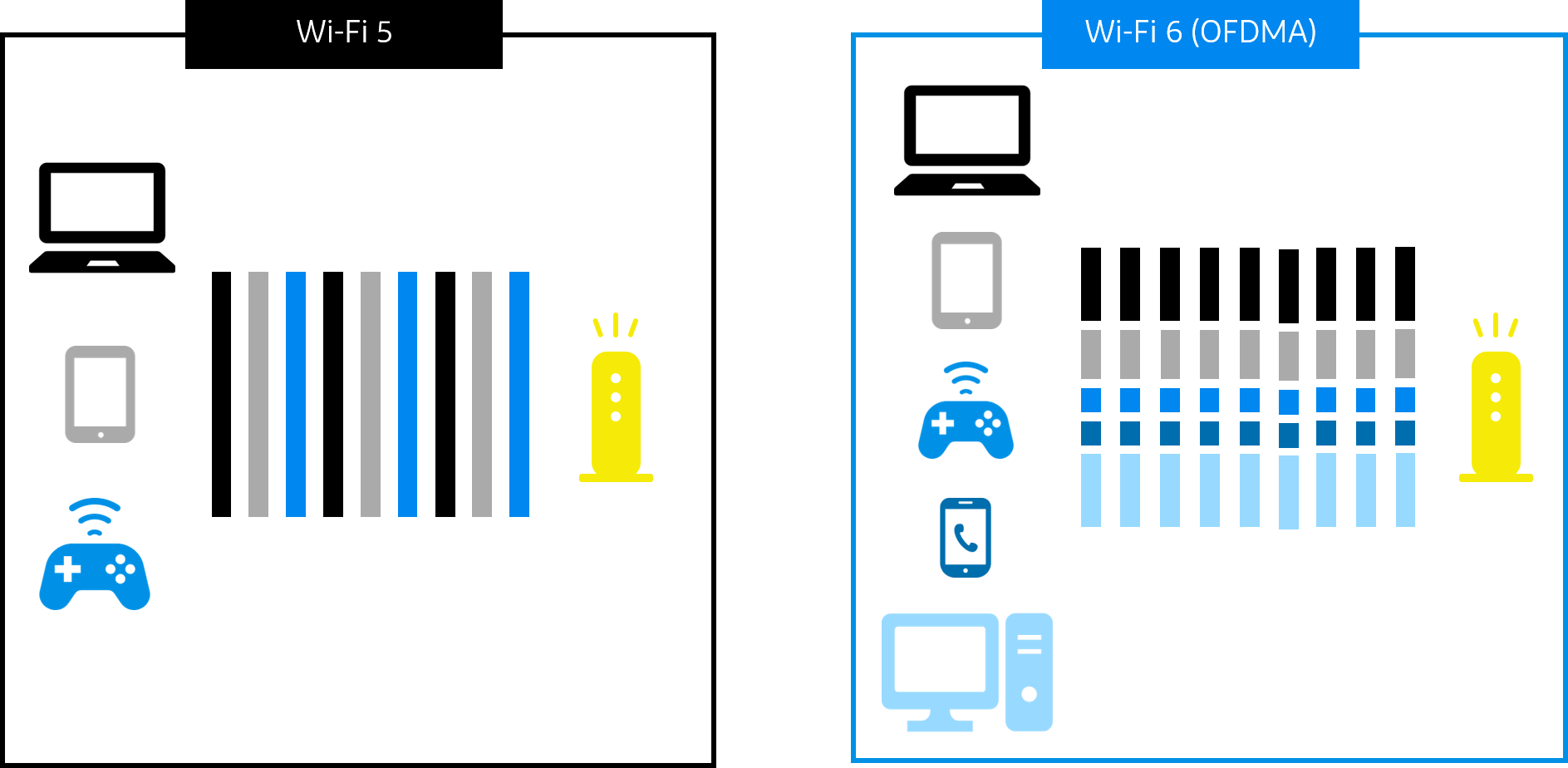
With Wi-Fi 5 and earlier Wi-Fi standards, if more devices are connected at the same time, the connection can become congested and slow.
Wi-Fi 6 uses a technology called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), which allows devices to share the airwaves so that they can be connected at the same time and not wait for each other. In the past, when a large number of devices were connected to Wi-Fi at the same time, it took a long time to download videos and images due to the congestion of the line. However, Wi-Fi 6's ODFMA technology enables stable communication even in environments where many devices are connected simultaneously, such as offices, restaurants, and event venues.
- Operating frequency range
Wi-Fi 6 uses two bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. While the 2.4 GHz band is not as fast as the 5 GHz band, it is more resistant to obstructions such as walls and doors, making it a frequency band that can support a wide range of applications. However, since the 2.4 GHz frequency band is also used for various devices such as microwave ovens and Bluetooth, radio interference may occur.
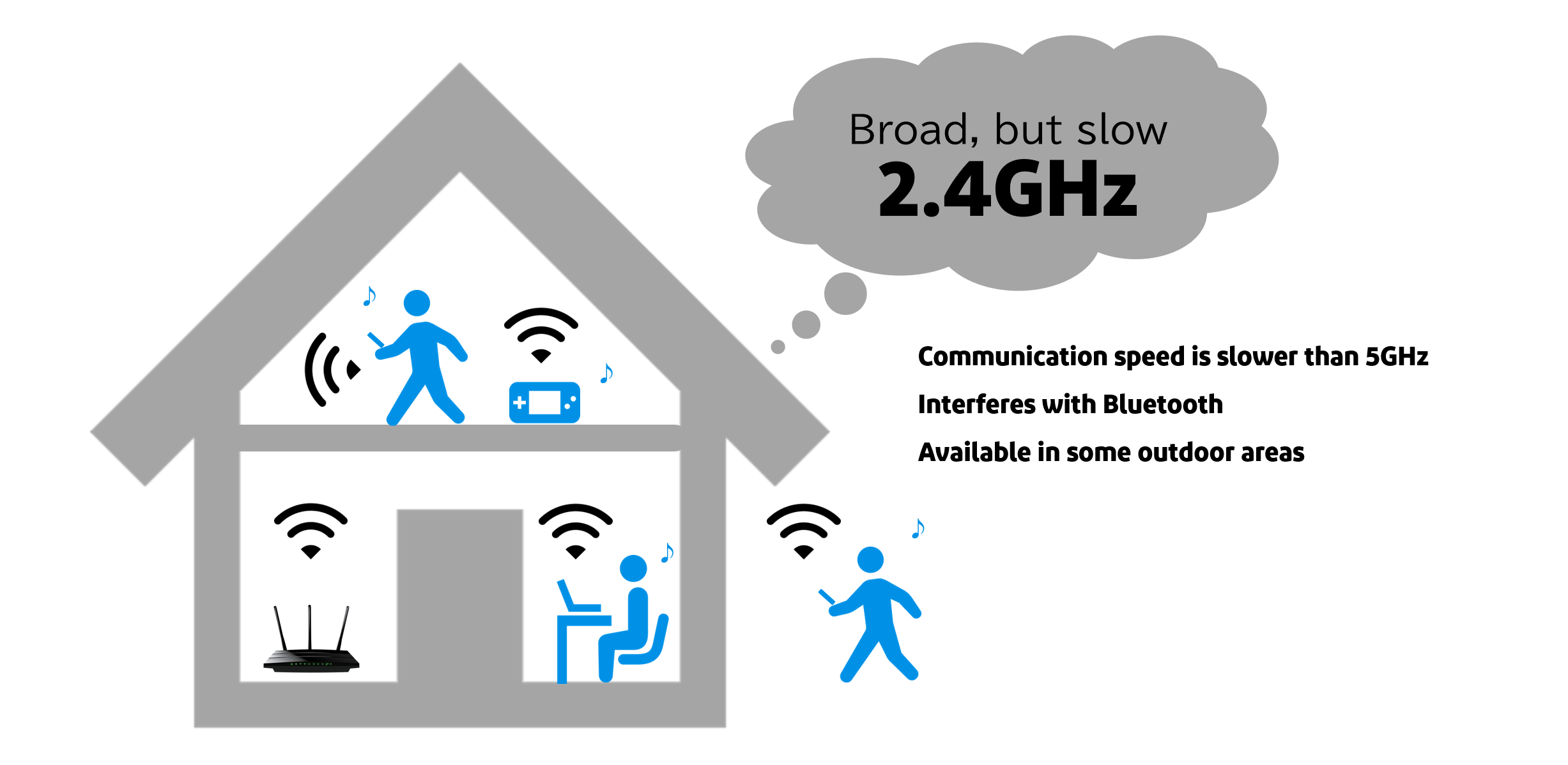
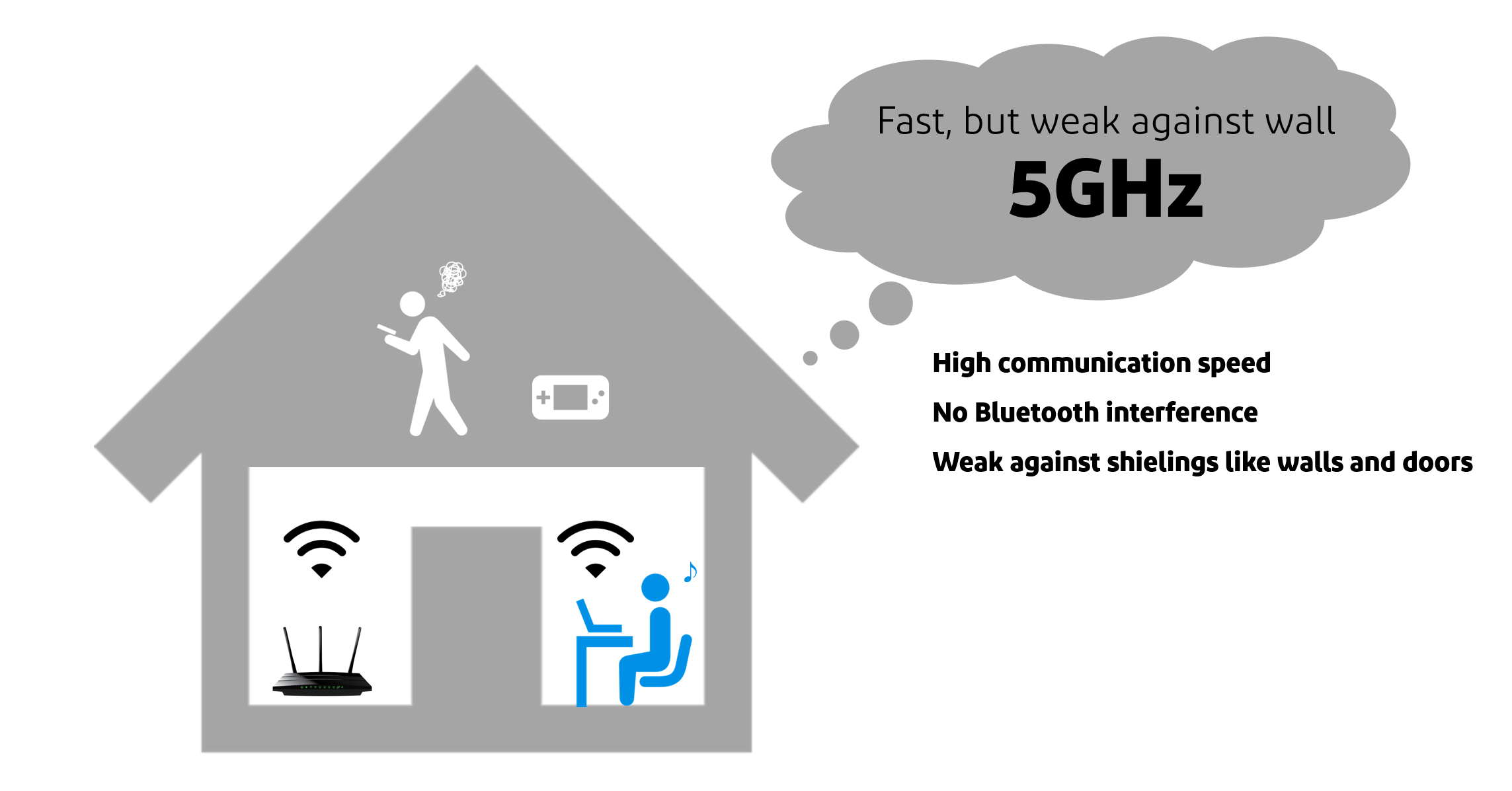
While 5 GHz has a higher transmission speed than 2.4 GHz, it is vulnerable to shielding such as walls and doors.
I-PEX offers an extensive line of micro RF connectors for Wi-Fi 6 / W-Fi 6E applications.

