What is USB?
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a standard for cables and connectors used to connect devices for digital communication and power supply purposes, with specifications and standards defined by the USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum, Inc.).
-
Relationship between high-speed data transfer and transmission distance
-
I-PEX connectors suitable for internal connection of USB4 transmission standard
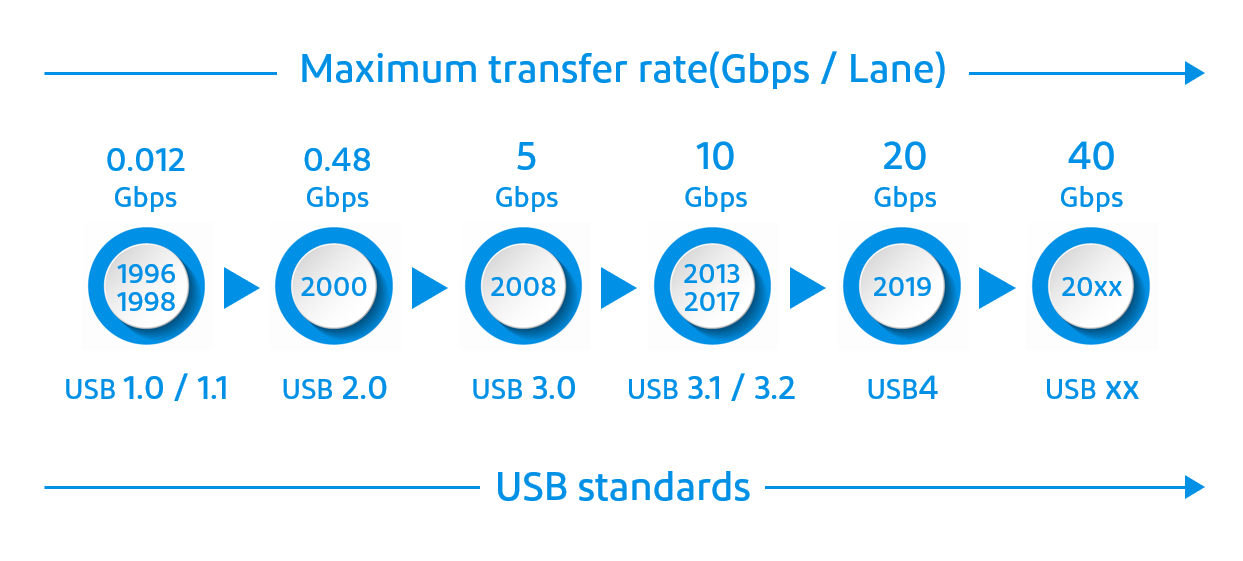
1. Types and generations of USB standards
Before the advent of the USB standard, different types of connectors were used for different purposes to connect PCs to external peripherals. In 1996, USB 1.0 was developed to unify the interface. Since then, the technical specifications have been updated, and recently, the USB4 standard with a maximum transfer rate of 20 Gbps/lane has been established. USB technology is expected to continue to improve in performance.
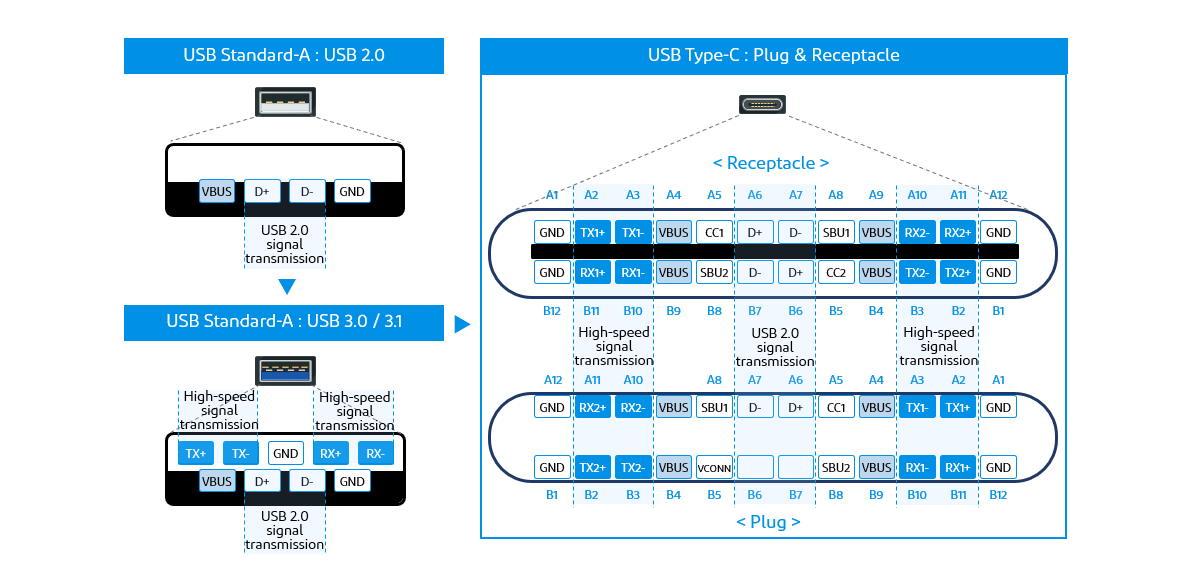
2. What is USB Type-C?
USB Type-C is one of the USB connector standards. It is a 24-pin connector for connecting USB-compatible devices with a cable. It is a high-performance external interface that is smaller than the conventional USB Standard-A, but allows reversible insertion and high-speed data transfer. In addition, a new USB Power Delivery standard has been added that can deliver up to 20V 5A (100W) of current.

Ultra-high speed data transfer
The USB 2.0 Standard-A connector had only one lane for signal transfer, with a maximum transfer rate of 0.48 Gbps/lane. The USB 3.0/3.1 Standard-A connector retains the USB 2.0 connector, but adds two new lanes for high-speed signal transfer, enabling bi-directional communication. Maximum data transfer speeds of up to 5 Gbps/lane for USB 3.0 and 10 Gbps/lane for USB 3.1 are supported. The USB Type-C connector has an additional two lanes for high-speed signal transfer, supporting the USB4 standard with a maximum transfer rate of 20 Gbps/lane.
3. Relationship between high-speed data transfer and transmission distance
The higher the speed of the transmitted signal, the greater the transmission loss, such as conductor loss and dielectric loss, etc., that occurs in the transmission path, making signal transmission more difficult.
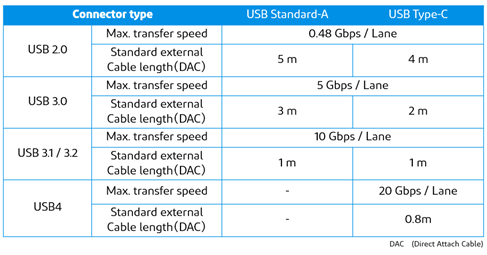
Therefore, depending on the transmission standards, there are reference specifications for the internal loss value called the loss budget. For example, in the case of the USB4 specification Ver. 1.0 [Thunderbolt 4], which is a 20 Gbps (10 GHz)/lane high-speed transmission, the loss budget is specified as -7.5 dB for each of the cable and device.
The longer the transmission distance, the greater the loss that occurs in the transmission path. High-speed signals such as USB4 can be transmitted by using a low-transmission-loss board if the transmission distance is to a certain extent. However, the longer the transmission distance, the greater the loss that occurs in the transmission path, and it becomes more difficult to transmit signals within the loss budget. Therefore, if the transmission path is long, it is necessary to take measures to suppress the loss that generated in the transmission path.

4. I-PEX connectors suitable for internal connection of USB4 transmission standard
Micro-coaxial connectors
-
CABLINE®-VS II
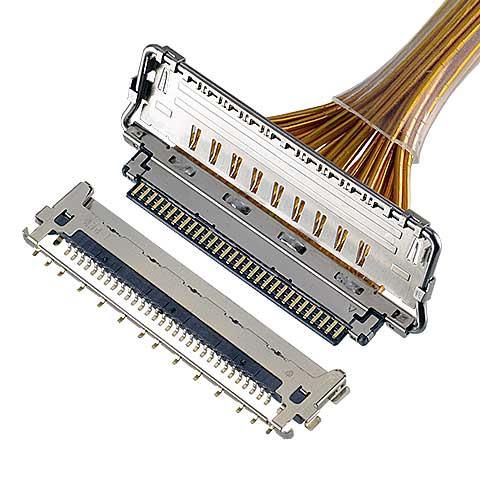

0.5 mm pitch, Horizontal mating type, Fully-shielded with mechanical lock, Suitable for high-data-rate transfer (20 Gbps/lane) -
CABLINE®-VS
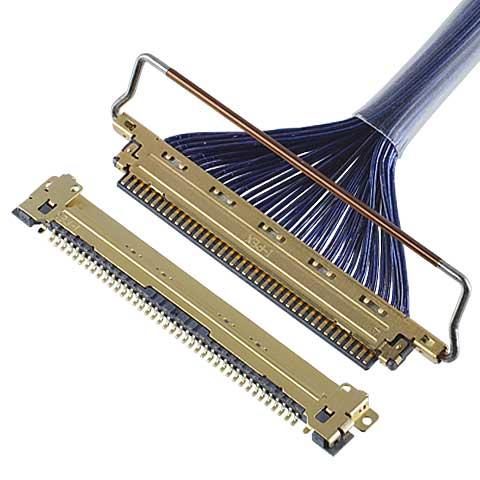

0.5 mm pitch, Horizontal mating type with mechanical lock (VESA standard connector) -
CABLINE®-UM
0.4 mm pitch, Right angle vertical mating type, Fully-shielded and multi-point ground, Mechanical lock, High-data-rate transfer (20 Gbps/lane) -
CABLINE®-CA II
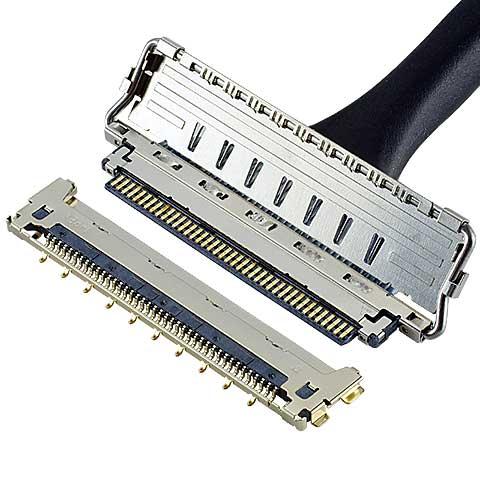

0.4 mm pitch, Horizontal mating type, Fully-shielded with mechanical lock, High-data-rate transfer (20 Gbps/lane) -
CABLINE®-CA II PLUS
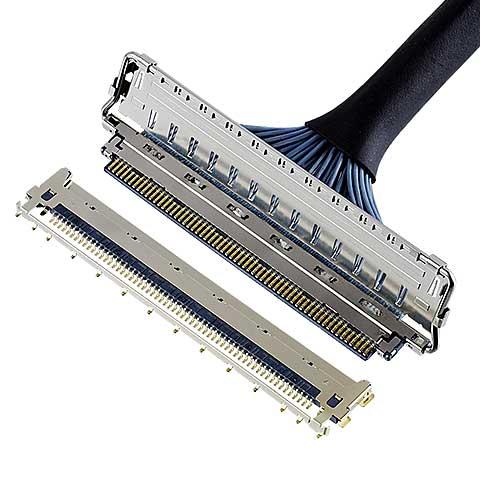

0.4 mm pitch, Horizontal mating type, Fully-shielded with mechanical lock, High-data-rate transfer (20 Gbps/lane)
- CABLINE®-CA
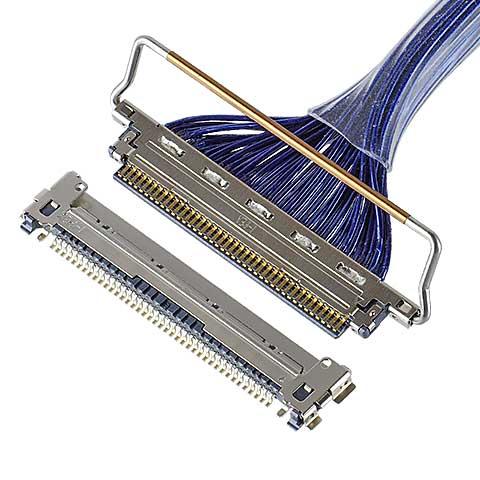

0.4 mm pitch, Horizontal mating type with mechanical lock (mating height : 1.10 mm max.)
-
CABLINE®-CAL
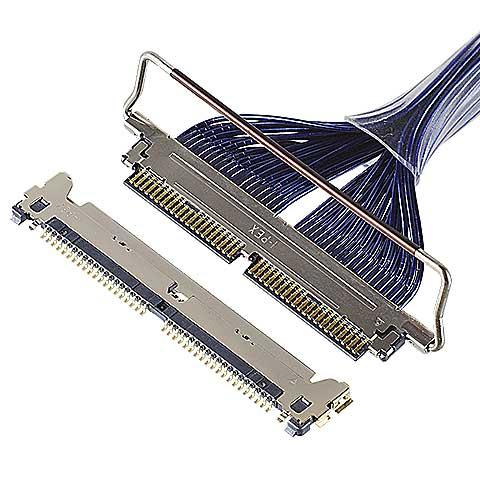

0.4 mm pitch, Horizontal mating type with mechanical lock (mating height : 0.8 mm max.)
FPC/FFC Connectors
- EVAFLEX® 5-HD
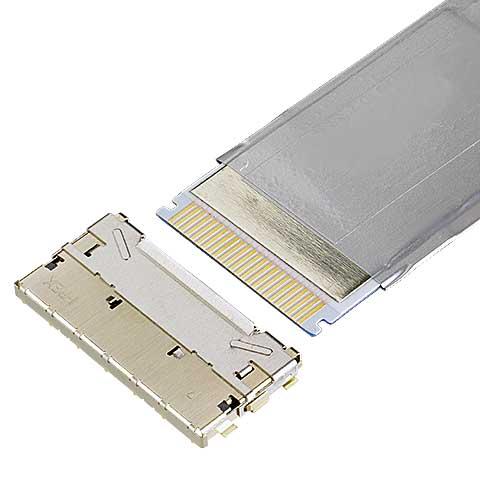

0.5 mm pitch, horizontal mate, Fully-shielded, high-speed, auto-locking
Board-to-Board (FPC) Connectors
-
NOVASTACK® 35-HDN
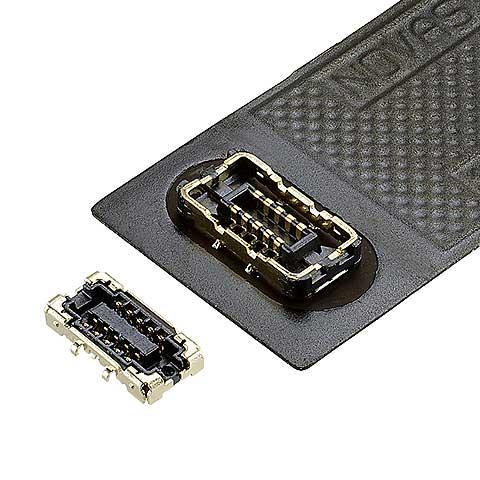

0.35 mm pitch, Fully-shielded and narrow design, Power supply is available with Corson Alloy contact, 0.7 mm height -
NOVASTACK® 35-HDP
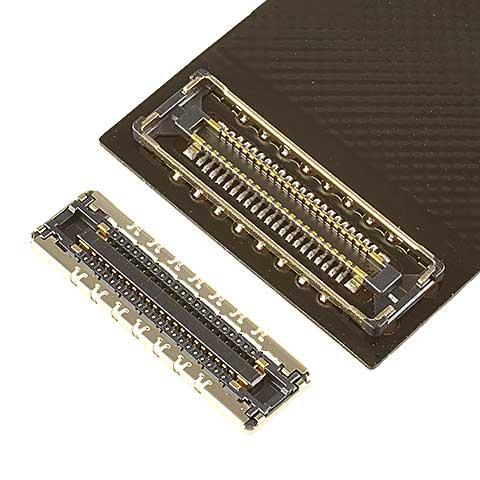
0.35 mm pitch, High-speed (20+ Gbps/lane) fully-shielded with power contacts, 0.7 mm height
Industry standard USB Type-C I/O connector
